Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles Tendonitis is commonly known as heel pain, which describes its key symptom. But there are several causes of heel pain. Pain is unpleasant and it makes walking uncomfortable and life miserable.
Pain, located in the Achilles Tendon, may be worse after rest or excessive activity. In the acute phase local swelling will be evident. In the chronic phase there may be the development of thickening and nodules.
Causes
• Degeneration of the Achilles Tendon caused by over-use or by bio-mechanical issues that are specific to the person.
• Excessive Pronation (inward rolling of foot)
• Tight or weak calf muscles.
• Reduced ankle range of motion.
• Over-use: too much training or too much training too soon .
• Continuous or long term use of, high heels, worn out or unsupportive sports shoes.
• In chronic cases it may be associated with people who lead sedentary lifestyles.
• In chronic cases, it may be associated with obesity or systemic conditions e.g. arthritis, cholesterol, diabetes and menopause.
These above issues must be considered and the real cause isolated, so that a treatment plan can be designed specifically for you, that will either correct or respond to the underlying cause. Once your situation is known, then it is important to resolve your concerns, know what treatment is necessary and why. This way you will feel confident in your treatment plan and actively pursue a pain free recovery.
Whatever the plan, it is a partnership between you and your practitioner with your health and wellbeing as the key goals.These above issues must be considered and the real cause isolated, so that a treatment plan can be designed specifically for you, that will either correct or respond to the underlying cause. Once your situation is known, then it is important to resolve your concerns, know what treatment is necessary and why. This way you will feel confident in your treatment plan and actively pursue a pain free recovery. Whatever the plan, it is a partnership between you and your practitioner with your health and wellbeing as the key goals.
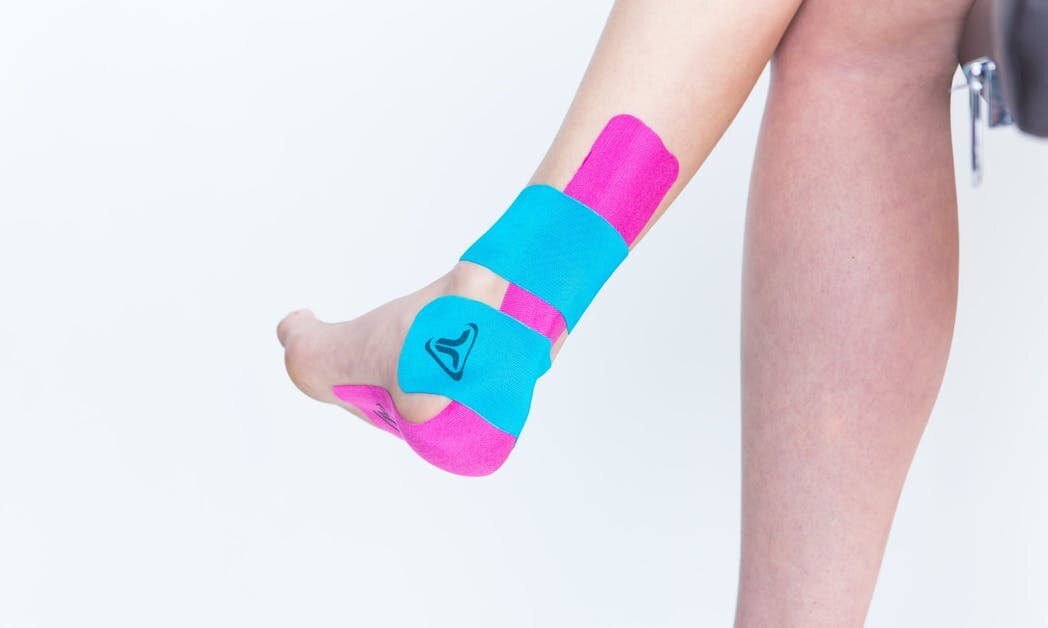
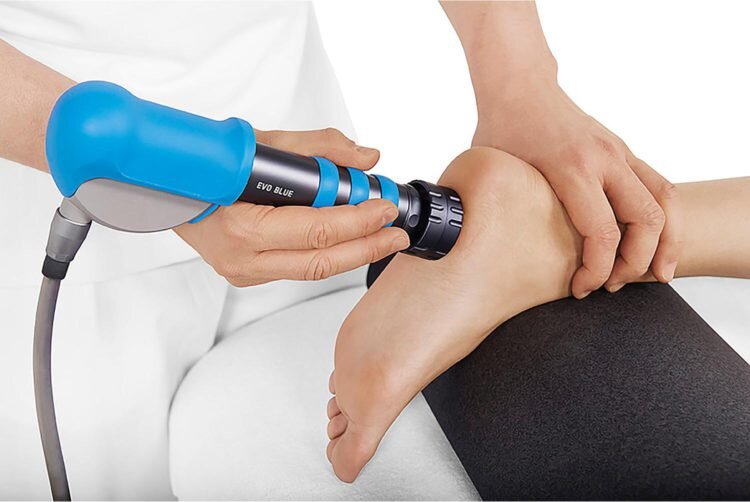
Treatment Options
Seek treatment as soon as possible. It will reduce down time, pain and the likelihood of complications like stress fractures and permanent damage.
Assessment and Diagnosis: Your podiatrist will look at your situation, diagnose the cause and the severity of the condition and discuss your lifestyle activity needs before doing anything. This process gathers the information required to tailor-make the treatment plan, that takes into account your specific needs. How long you have had the conditions, your foot function and your activity level are criteria that must be understood first.
• R.E.S.T. Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
• Ongoing pain relief through compression taping and medicinal Pain relief.
• An Effective Rehabilitation Program (acute cases) with a gentle and gradual return to normal activities.
• Remedial Massage reduces inflammation
• Prolotherapy for pain management and to strengthen the tendon.
• Dry Needling to decrease muscle tension.
• FS6 compression socks for day/night use to reduce pain and increase support.
• Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for pain relief and faster recovery
• Orthotic Therapy may be prescribed.
• Cortisone Injection under an ultrasound guided injection
• Referral for X-rays, ultra-sound or specialists for more research if warranted.
• Surgical Intervention (last resort only)
Prevention
Address underlying systemic issues causing the problem. They will make it worse over time. These exercises will help ease the discomfort and condition...
1. Calf stretches: 10 seconds x 10 repetitions twice daily to extend shortened muscles.
2. Strengthen your calk muscles. Your podiatrist can help you with ideas.
3. Lose Weight if needed. Your feet wear the brunt of everything! High impact activity may generate
g-forces on the feet up to 6x’s your body weight. Sop excess weight is going to create issues.
4. Be regular with your Orthotic check ups to ensure your devices remain in a condition that will protect you.
Have several pairs that are inserted into different shoes, as this helps encourage compliance.
5. Heel lifts that shorten the Achilles Tendon and prevent overloading may be useful.
6. Wear supportive footwear that is suited to your foot type. Our podiatrists can help with this.
Take the first step!